| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 산책하기 좋은 곳
- 졸업 작품 소재
- 표준 라이브러리 함수
- 프로젝트
- c#
- 언제나휴일
- 동영상 강의
- 원격 제어 프로그램
- 추천
- 클래스 다이어그램
- C++
- 소스 코드
- Windows Forms
- 언제나 휴일
- 표준 입출력
- 네트워크 프로그래밍
- 무료 동영상 강의
- 독립기념관
- 알고리즘
- 동영상
- 파이썬
- 강의
- c언어
- 안드로이드 앱 개발
- 유튜브 동영상 강의
- 실습으로 다지는 c#
- 캡슐화
- 충남 천안
- 실습
- 소켓 통신
- Today
- Total
목록전체 글 (365)
프로그래밍 언어 및 기술 [언제나휴일]
요구 사항을 파악한 후에 유즈케이스 다이어그램을 작성하였으면 이 둘 간의 매핑 테이블을 만들어 보세요. 이를 통해 어떠한 요구 사항이 어느 유즈케이스에 반영했는지 파악하기 쉽고 반영하지 않은 요구 사항이 있는지 확인하기 쉬워집니다. 하나의 요구 사항을 반영하는 여러 개의 유즈케이스가 있을 수 있고 여러 개의 요구 사항을 반영하는 하나의 유즈케이스가 있을 수 있습니다. 그리고 품질에 관한 요구 사항을 반영하는 특정 유즈케이스가 없을 수도 있습니다. 요구명관련 Usecase웹 로봇WebCollect분석기Morphemepares색인기MakeInvertedFile랭커Ranking관리SetInterval, Start, Stop, AddSeedSite검색Search결합성품질 요구 사항임재사용성품질 요구 사항임시스..
 2. 2 유즈케이스 다이어그램
2. 2 유즈케이스 다이어그램
유즈케이스 다이어그램은 시스템에서 구현해야 할 기능을 개괄적으로 보여주기 위해서 수행합니다. 이를 통해 시스템이 처리해야 할 일과 외부에서 수행할 일을 결정하고 어떠한 사용자와 시스템과 상호 작용하는지를 결정합니다. 이를 위해 먼저 시스템과 상호 작용하는 사용자와 외부 시스템을 찾는 작업을 수행합니다. 유즈케이스 다이어그램에서는 시스템과 상호 작용하는 사용자와 외부 시스템을 액터라고 말합니다. 그리고 액터가 어떨 때 우리 시스템을 사용하는지 우리 시스템이 언제 액터를 사용하는지를 결정합니다. 그리고 이를 유즈케이스로 나타냅니다. Usecase 다이어그램은 액터와 Usecase, 관계를 표현합니다. 2.2.1 액터 개요 액터는 시스템과 상호 작용하는 사용자와 외부 시스템을 말합니다. EH..
요구 분석 및 정의 단계에서는 시스템에서 제공해야 할 비지니스와 이해관계자의 요구 사항을 정확히 이해하는 작업이 필요합니다. 이를 위해 이해관계자의 요구 사항을 수집하고 이해해야 합니다. 그리고 수집한 요구사항을 바탕으로 시스템에서 제공해야 할 기능을 개괄적으로 파악하고 결정해야 합니다. 이 책에서는 어떠한 이해관계자가 있는지에 관한 조사와 이를 통해 요구 사항을 수집하는 부분은 간단히 요구 리스트를 보여주는 것으로 끝낼 것입니다. 대신 요구 리스트를 바탕으로 시스템에서 제공해야 할 기능을 파악하고 결정하기 위해서 Usecase 다이어그램을 작성하고 요구 사항과 Usecase 매핑 테이블을 작성하기로 할게요. 2.1 요구리스트 요구명설명구분웹 로봇웹 페이지를 수집할 수 있어야 합니다.기능분석기수집된..
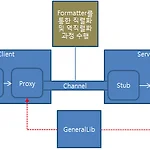 1. 7 .NET 리모팅
1. 7 .NET 리모팅
.NET 리모팅 기술은 서버 측에 있는 개체를 클라이언트 측에서 마치 자신에게 있는 개체를 사용하는 것처럼 사용할 수 있게 서비스를 하는 기술입니다. .NET 리모팅 서비스를 위해서는 서비스를 제공하는 서버와 서비스를 제공받는 클라이언트가 필요하며 서버 측에서 클라이언트에 제공하는 개체를 정의한 클래스 라이브러리가 필요합니다. 서버 측에서 클라이언트에 제공하는 개체는 MashalByReference에서 파생한 개체로 원격 개체라고 말합니다. 서버 측에서는 채널을 등록하여 원격 개체를 사용할 수 있게 등록합니다. 클라이언트 측에서는 서버 측 채널에 접근하여 원격 개체를 참조하여 사용하는데 클라이언트 측에서 원격 개체를 참조하여 사용할 수 있는 개체를 Proxy 개체라 부릅니다. 클라이언트 측에서 P..
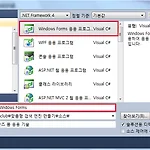 1. 6 Windows Form
1. 6 Windows Form
이번에는 간단하게 Windows Form 응용 프로그램을 만들기 위해 필요한 기술을 알아봅시다. 먼저 윈도우즈 응용 프로그램을 만들기 위해 Windows Forms 응용 프로그램 템플릿을 선택합니다. Windows Forms 응용 프로젝트를 생성하면 기본적으로 진입점이 있는 Program.cs 파일과 MainForm에 관한 두 개의 소스 파일로 Form1.cs와 Form1.Designer.cs이 만들어집니다. Program.cs 파일에는 Form1 개체를 생성하여 닫힐 때까지 수행할 수 있는 코드 등이 자동으로 만들어진 상태입니다. 특이 사항이 없으면 Windows Forms 응용 프로그램을 제작하면서 이 부분을 수정할 필요는 없습니다. 그리고 Form1.cs는 개발자가 작성할 부분이며 Form1.De..
